MICROGAS
WARNINGS

General description of the device
Medical devices in the Microgas family are on the market under the different trade names:
- Microgas – SF6 mix 20%.
- Microgas – Pure SF6
- Microgas – C2F6 mix 16%.
- Microgas – Pure C2F6
- Microgas – C3F8 mix 12%.
- Microgas – Pure C3F8
Microgas family devices consist of an aluminum canister with a 50cc capacity filled with pure gas or mixed with nitrogen.
Along with the gas-filled canister, in the tyvek bag is contained:
- 0.2 um sterilizing filter
- Needle 27 G and needle 30 G for infusion
- 3-way tap to regulate the infusion
- 60 ml syringe for infusion
Medical devices in the Microgas family are classified IIb, according to Rule 8. As implantable, with short- and long-term residence time.
Directions for use.
Most of the information summarized in this section can be obtained from the instructions for use delivered with the medical device.
Microgases are high molecular weight gases intended to replace the vitreous humor in vitrectomy surgeries.
The average residence time in the eye varies depending on the gas used: SF6 1-2 weeks, C2F6 4-5 weeks, C3F8 6-8 weeks.
The device should only be used in sterile field by professionals. Gas should be inserted into the vitreous cavity after carefully removing the central and peripheral vitreous.
Pure gases should never be used alone, but it is always advisable to mix the gas with air; alternatively, already mixed gases can be used. The recommended mixing percentage is indicated on the syringe itself and is the same as that used in mixing with nitrogen.
The device is contained in a tyvek pouch along with accessories; pouch and contents are EtO sterilized. The gas contained in the canister is not sterile: accessories include a sterilizing filter, to be placed between the canister and the syringe when filling the gas syringe. See the image below for further clarification.
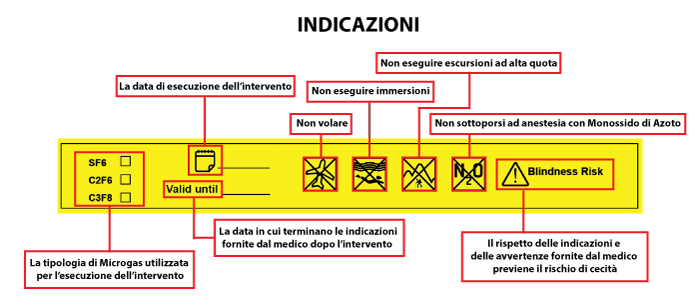
After surgery, variable device information should be reported in the medical record by application of pre-filled adhesive labels provided with the DM.
The implant card provided must be filled out by entering the patient’s name, date of operation, name of the facility, and name of the doctor who performed the operation.
Contraindications
The contraindications below are also available in the package insert.
- Do not inject into the vitreous
- In the case of anesthesia with nitrous oxide, inhalation of the anesthetic should be stopped at least 15 minutes before the product is used.
The medical device should only be used by a trained retinal vitreous surgeon in a sterile field.
Complications
The residual risks associated with the use of DM are the same as in vitreoretinal surgeries.
Some of the postoperative complications could be:
- Neovascular glaucoma
- Cataracts
- Lenticular opacity
- Keratopathies
- Hypertone (increased eye pressure)
- Transient or permanent decrease in eye pressure
- Alterations of the macula
- Choroid detachment
- Retinal tear and/or relapsed retinal detachment
It is the responsibility of the surgeon to properly inform the patient of the risks-benefits of the operation.
WARNINGS
- Do not use the device for uses other than those indicated.
- The medical device is disposable. The presence of multidose is intended only as a precautionary measure to provide a backup in case of procedural problems in the operating room.
- Use only in sterile field.
- Do not use the product after the expiration date.
- Make sure the packaging is intact: sterility is guaranteed if the packaging is intact. Do not use the device if the packaging is damaged.
- Do not re-sterilize accessories. Re-sterilization could lead to material degradation processes.
- The contained accessories are sterile and disposable. Reuse of accessories can lead to contamination events
bacteria, with serious consequences for the patient. - The gas in the canister is NOT sterile. Sterilize with the filter given in the package.
- Pure gas should be mixed with sterile air: the suggested concentration for SF6/C2F6/C3F8 is in the range of 20% / 16% / 12%.
- Make sure that there is no free vitreous or that it may be pushed by gas into abnormal positions, especially in aphakics.
- Check for proper papillary blood supply and any optic nerve compression by suspending the infusion immediately if necessary.
- If the eye is leaky make sure that there is an escape route while injecting the substance in order to avoid dangerous ocular hypertension.
- In case of hypertone >30 mmHg operate a direct reduction of the gas contained in the bulb within 10 minutes.
- he injected gas is an expandable mixture: check the eye pressure every hour for the first 6 hours and frequently for the next 36 hours.
- Any use of infusion machines should be limited to the use of equipment approved for ophthalmic use. It is the physician’s responsibility to verify compatibility between the device and the specifications of the equipment itself.
- In addition, in order to avoid serious adverse effects, it is the responsibility of the physician specializing in vitreoretinal surgery.
- Inform the patient about behaviors to avoid after surgery. To avoid dangerous ocular hypertension, patients should not expose themselves to changes in pressure, such as when traveling by air, in the mountains at high altitudes or diving; special attention should also be paid to sudden changes in environmental temperature (e.g., entering an overheated car in summertime).
- Fill out and give the implantable card to the patient.
- Attach the bracelet to the patient’s wrist.